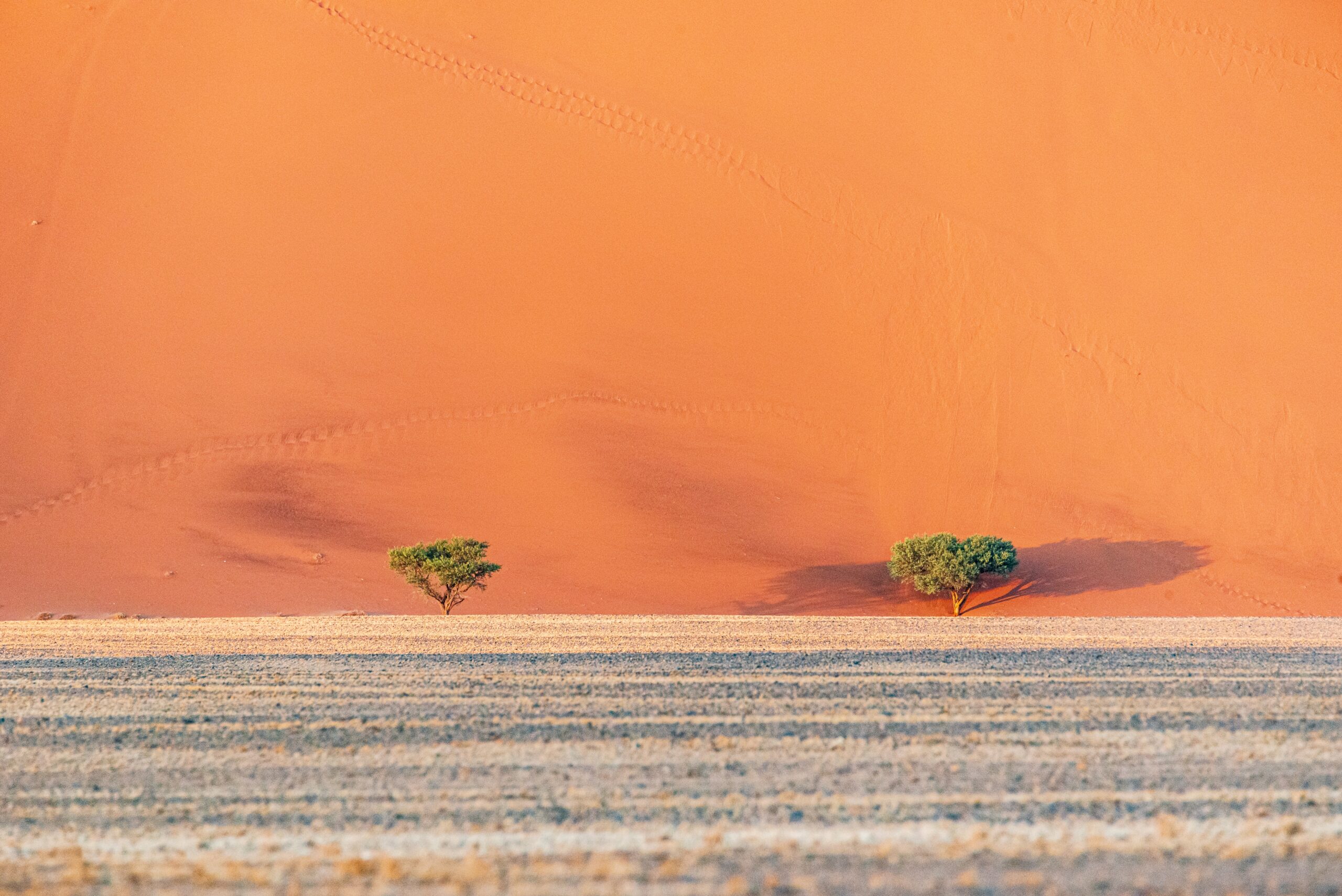
Immerse yourself in the captivating landscapes of the Kalahari and Namib Desert. These iconic African terrains, stretching over millions of acres, are not just barren lands but cradles of life, home to a diverse array of unique species. The biodiversity of the Kalahari and Namib Deserts is a testament to nature’s resilience, with lifeforms having adapted to thrive in some of the harshest conditions on Earth. The importance of biodiversity extends beyond the boundaries of deserts. It plays a critical role in maintaining ecological balance, offering lessons in sustainability, and serving as a reservoir of genetic resources. In this blog post, we will delve into the remarkable biodiversity of these deserts, revealing the hidden treasures of these seemingly desolate expanses.
The Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert, a vast semi-arid savannah, stretches over 900,000 square kilometers across Southern Africa. This massive expanse of land covers a significant area of Botswana and extends into Namibia and South Africa. Despite not being a true desert, the Kalahari exhibits the characteristics of one, with its extensive sand sheets, towering dunes, and occasional salt pans.
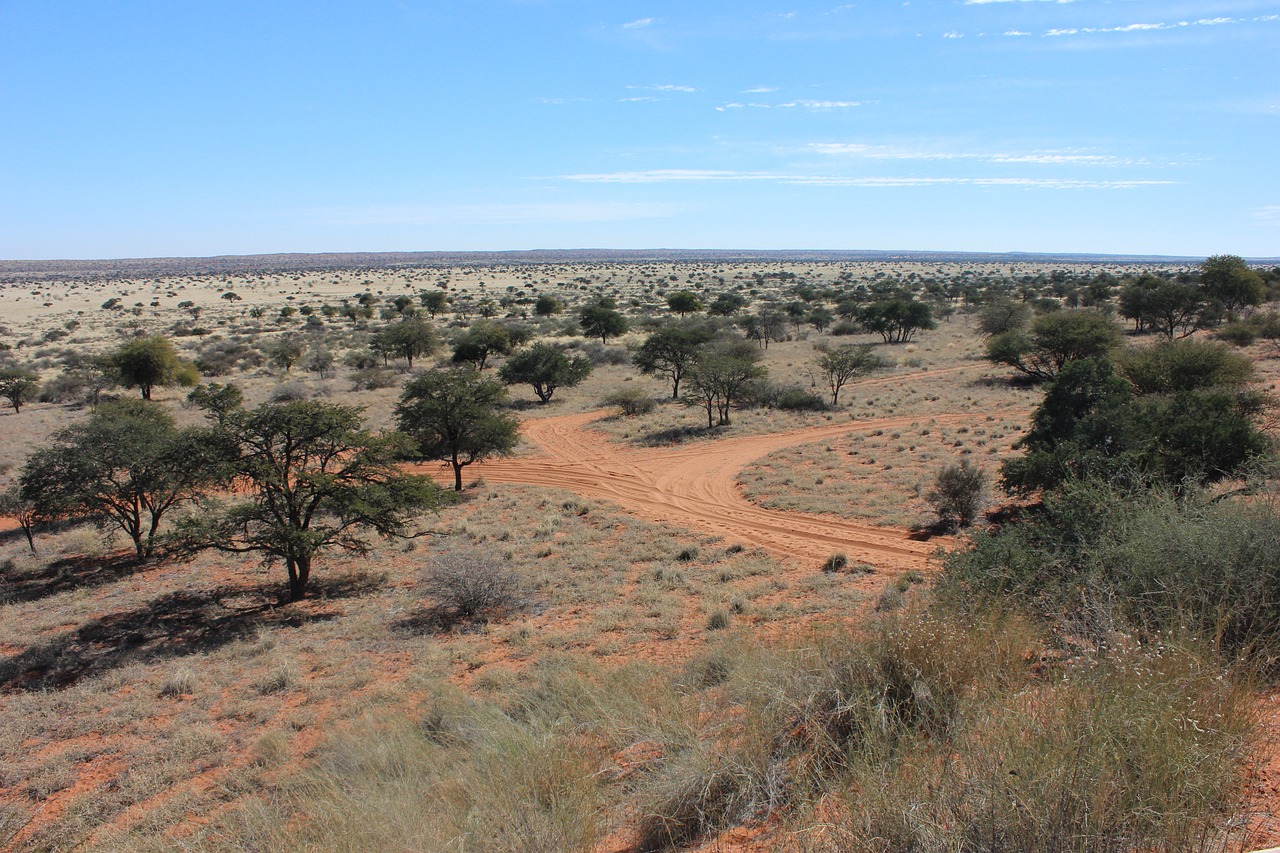

This intriguing landscape is home to an array of unique species that have adapted to its harsh conditions. Notable among them are the hardy gemsbok antelope and the striking Kalahari lion. The desert also hosts a variety of plant species like the camelthorn tree and Devil’s Claw, a plant well-known for its medicinal properties.
However, biodiversity is under threat. Overgrazing, climate change, and human encroachment pose significant challenges to the Kalahari’s unique ecosystem, threatening its distinct flora and fauna. It’s a reminder of the delicate balance of life in this seemingly inhospitable environment and the urgent need for conservation efforts.
Map Of Kalahari Desert Map

The vast Kalahari Desert, which extends across numerous nations in Southern Africa, is depicted geographically on the Kalahari Desert map. The desert, which spans 900,000 square kilometers, can be found in major parts of Botswana, Namibia, and South Africa. It extends into Zimbabwe, Zambia, and Angola.
The Namib Desert
The Namib Desert, which is found in Southern Africa’s Atlantic region, runs for more than 2,000 kilometers from Angola through Namibia and into South Africa. The Namib is a region with harsh weather, little rain, and tall sand dunes. It also has coastal fog.
Despite these challenging circumstances, a range of unusual organisms that have adapted to the desert’s climate can be found there. Numerous creatures can be found in the desert, such the Welwitschia plant, which can live its entire life with only two leaves, and the Namib Desert beetle, which collects water from morning fogs. The desert elephants, which have long legs and are well adapted to the dry climate, and sidewinder snakes are among the other prominent residents.
However, the biodiversity of the Namib Desert faces The delicate balance of this ecosystem can be upset by increases in temperature and variations in precipitation patterns, and human activities like mining and tourism can degrade or destroy habitats. Sustainable practices and conservation initiatives are necessary to protect the unique biodiversity of the Namib Desert.
Map Of Namib Desert
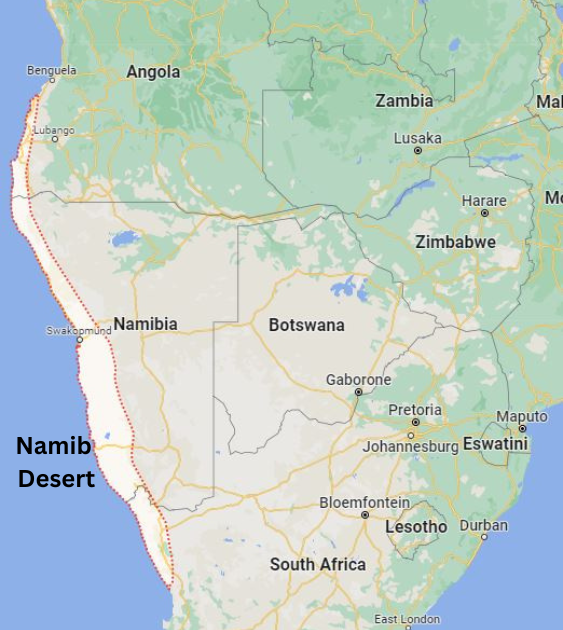
The Namib Desert is one of the oldest and largest deserts in the world, estimated to be between 55 to 80 million years old. It stretches over 2,000 kilometers along the Atlantic coasts of Angola, Namibia, and South Africa, spanning from the Carunjamba River in Angola, southward to the Olifants River in Western Cape, South Africa.
Comparing Biodiversity in the Kalahari and Namib Deserts
The Kalahari and Namib Deserts exhibit different amounts of biodiversity despite their harsh environments because of their distinctive features. The Kalahari, a semi-arid savannah, contains a wider variety of plants and animals than the Namib, a real desert. The Kalahari receives slightly more annual rainfall, which supports a wider variety of species.
In both environments, there exist organisms that exhibit extraordinary survival adaptations. The Kalahari is home to both the Kalahari lion, which lives in smaller groups and has wider territory, and the gemsbok antelope, which can go for extended periods of time without water. In the Namib, desert beetles collect water from early morning fogs, while Welwitschia plants can survive on just two leaves.
Despite their biodiversity, both are at risk from human activity and climate change. These deserts exhibit such vast variety despite their similarities, demonstrating the adaptability of life in harsh environments and the significance of protecting these ecosystems.
Also read: Fun Facts About the Gobi Desert Asia’s Biggest Desert
Conservation Efforts
Due to the Kalahari and Namib Deserts’ global relevance, local and international conservation efforts are being made there. The Tswalu and Khamab Kalahari Reserves are in the forefront of protecting the Kalahari’s unique habitats and serving as sanctuaries for a range of animals and plants. These reserves strive to restore the natural processes that characterize Kalahari habitats while providing a safe haven for threatened species.
In the Namib Desert, Brink Biological Research conducts research to save the environment and assure its sustainability. By using the reserve as a research location, they advance our knowledge of this distinctive desert ecosystem.
Readers can participate in these efforts in a number of different ways. Safaris focused on conservation provide a chance to see wildlife and learn about the crucial work being done to protect these areas. Additionally, contributing to or volunteering for organizations engaged in these endeavors can have a big impact. Additionally, raising public awareness of these distinctive ecosystems’ problems and challenges can aid in their preservation.
Takeaways:
The adaptability of life in even the harshest settings is demonstrated by the Kalahari and Namib Desert. Numerous species have developed exceptional means of surviving in these settings, ranging from the Kalahari’s gemsbok antelope, which can go for extended periods without water, to the Namib Desert beetle, which collects water from the morning fogs. These environments are in danger due to climate change and human activity, which highlights the necessity for conservation efforts.
We protect the biodiversity of our planet, aid in maintaining a stable climate, and safeguard these breathtaking vistas for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Kalahari desert in which country?
Located in Southern Africa, the Kalahari Desert extends across three countries. Botswana, Namibia and South Africa
Where is the Namib desert?
The Namib Desert, a gem of nature’s beauty, stretches along the Atlantic coastline of Africa. This vast expanse extends from Namibe in Angola, across Namibia, and reaches into South Africa.
Why is the Kalahari Desert so famous?
The Kalahari Desert is so famous for its unique wildlife, beautiful landscapes, cultural significance, national parks, scientific research and adventure tourism
What animals in the Kalahari Desert can be found?
These are the famous animals of the Kalahari Desert: Lions, Meerkats, African Wild Dogs, Springboks and Gemsboks, Cheetahs, Brown Hyenas ,Various Bird Species and Reptiles.
Which parks are located in the Kalahari Desert?
The closest national parks to the Kalahari Desert are Central Kalahari National Park and Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park.

